 Long-term fairness analysis framework
Long-term fairness analysis framework
Abstract
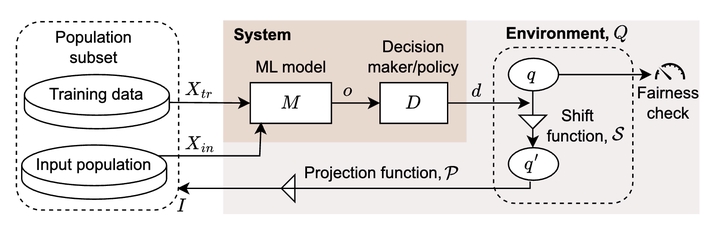
Algorithmic fairness of machine learning (ML) models has raised significant concern in the recent years. Many testing, verification, and bias mitigation techniques have been proposed to identify and reduce fairness issues in ML models. The existing methods are model-centric and designed to detect fairness issues under static settings. However, many ML-enabled systems operate in a dynamic environment where the predictive decisions made by the system impact the environment, which in turn affects future decision-making. Such a self-reinforcing feedback loop can cause fairness violations in the long term, even if the immediate outcomes are fair. In this paper, we propose a simulation-based framework called FairSense to detect and analyze long-term unfairness in ML-enabled systems. Given a fairness requirement, FairSense performs Monte-Carlo simulation to enumerate evolution traces for each system configuration. Then, FairSense performs sensitivity analysis on the space of possible configurations to understand the impact of design options and environmental factors on the long-term fairness of the system. We demonstrate FairSense’s potential utility through three real-world case studies: Loan lending, opioids risk scoring, and predictive policing.